What Is a Coil What Is a Glazeware for Art
BASICS
Clay is an earthy cloth of fine grained minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter.
Pottery tin be created without the use of a potter's wheel. The potter's wheel did not appear in history until only iv 000 years ago. The chief construction methods were compression and curlicue methods.
Clay has been used for many things throughout homo history: a writing surface, building material, coin, storage containers, cooking vessels and serving plates, electronic device parts, ceramic shields or tiles are used on space ships. Ceramics is a major tool for dating cultures in archeology studies.
the three paw-building techniques
pinch
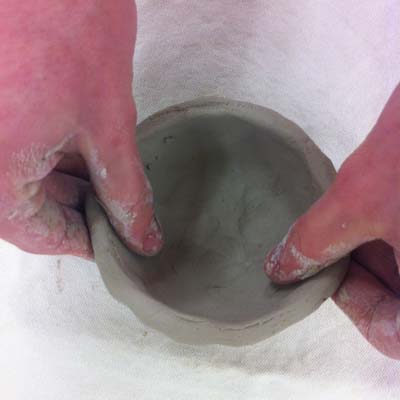
Pinch pots are created by using your easily to shape the dirt. Pinch pots are some of the oldest archaeological artifacts found on the planet.
- Brainstorm past forming a smoothen ball that fits in your palm (fist size).
- Printing the pollex into the center half-way to the bottom.
- Revolve the ball while pressing the walls out evenly with the other mitt.
curlicue

Whorl pots are created past pressing coils of clay together.
- Keeping the fingers apartment, form clay into sausage shapes.
- Roll them into ropes (coils)
1/four" to one/2" thick - Coils are pressed together creating a design. Gaps are filled in with small balls of dirt.
- Inside of the wall tin be smoothed.
- Join the walls & the bottom.
slab

The slab building technique involves rolling out clay to an even thickness - normally one cm - then cutting shapes, folding, angle, manipulating and joining together to form a finished object.
- Roll slabs of clay
- Cut out the sides
- Join the sides (score and slip!!)
- Attach the bottom
- Cut out the excess clay from the bottom slab.
Other techniques include:
wheel throwing, relief (high, low, sunken), mold making & slip casting, carving, sculpting, etc.
(remove air bubbles)

throw
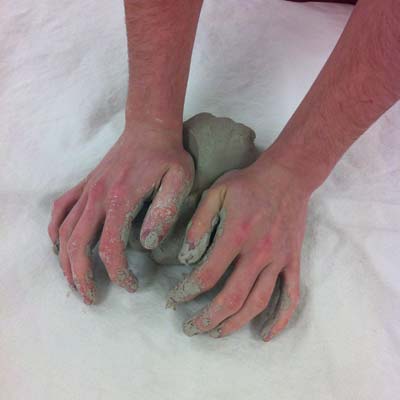

wedge

vanquish to class a ball
drying stages of dirt

slip
(liquid form of clay)
casting and cementing pieces

plastic
wedging, manipulating, sculpting,
throwing on the bike...

leather hard
well-nigh decorating is done, carving, stamping, building, etc..

bone dry
the driest phase of dirt, 0% moisture, prepare for bisque firing
firing stages

greenware
unfired pottery that is os dry (most fragile country)

bisqueware (bisque)
unglazed pottery that has been
fired once

glazeware
ware that has glaze applied and is waiting to be glaze fired
joining pieces

1. score
Roughen both surfaces that you lot are joining. Use a cantankerous-hatching design. Use a needle tool, wedge tool with "teeth", etc.

2. skid
Apply enough slip to both surfaces. Slip volition "cement" the pieces together as a glue.

3. rock & press
Stone back and along while applying some pressure on the slice. This will ensure that the skid will fill in all gaps and removes air pockets.
tools

cut-off wire
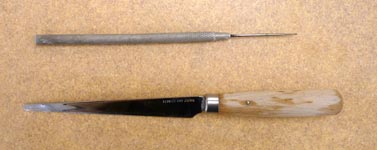
needle tool and fettling knife

modeling tools

rolling pivot and guides
drying
Clay project should dry out for at least vii days before bisque firing to ensure it does non accident upwards in the kiln.
Moisture (sudden change of h2o into steam) and air bubbles (trapped air expands) tin crusade the explosion.
firing
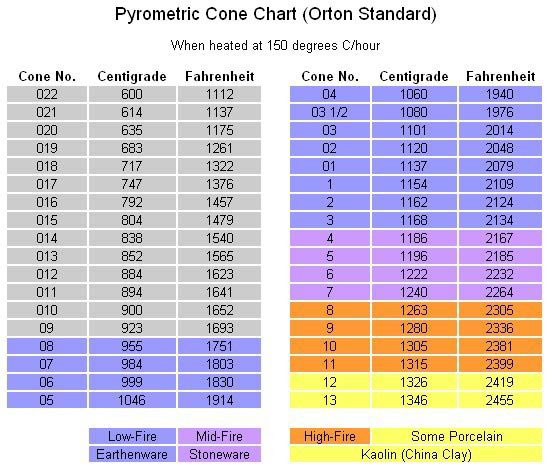
bisque firing
nosotros use depression-fire clay
Cone 04
Temperature 1940 F
glaze firing
we employ by and large depression-fire glazes
Cone 05-06
Temperature 1830-1914 F
glazing
- employ at to the lowest degree iii coats
- utilize coats evenly, wait for a coat to dry earlier applying the next i
- do not apply glaze on a bottom surface - the one that will be in contact with the kiln'south shelf.
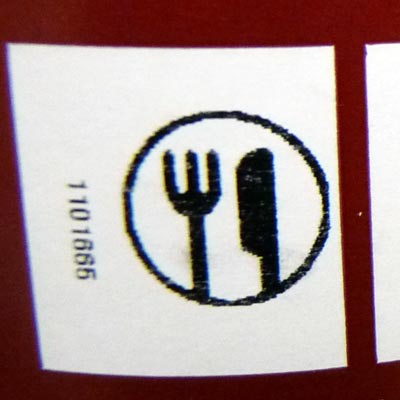
wipe it clean with a wet sponge before turning in for glaze firing - if your finished piece volition be in contact with food - wait for food safe marker on a glaze jar.
All glazes that are safe for food contact are labeled with one of the following signs:


the ten golden rules of ceramics
- Clay must be thoroughly covered up with a plastic bag to keep it from drying out. This applies to works in process and moist clay.
- Clay dust can be harmful if y'all are exposed to it for long periods of time, so continue your area make clean, clay scraps off the floor and clean with h2o and sponge.
- Clay should be no thicker than your thumb.
- In society for dirt to stick together information technology must be scored and and slipped together while the clay is moist (plastic) or leather hard.
- Wedge dirt to remove air bubbles, accomplish uniform consistency, and to line up the clay particles.
- Trapped air can cause dirt to explode. So hollow out sculptural forms and put needle holes through enclosed forms for air to escape.
- Don't glaze the lesser of the piece.
- Launder the slice before glazing.
- Handle your projection with two hands at all times. In other words - exist careful! - it'south your hard work.
- NEVER handle another person'south piece of work even if it looks absurd!
Source: https://juliannakunstler.com/ceramics1.php
0 Response to "What Is a Coil What Is a Glazeware for Art"
Post a Comment